
Is Hydrogen Electrification a Façade Deployment and Superficial Engagement?
PESTECH recently participated in the Green Hydrogen Conference, a gathering focused on examining and promoting the significance of green hydrogen in transforming the nation's economy. Attendees include policymakers, industry frontrunners, academic researchers, and stakeholders, all with the aim of cultivating collaboration and exchanging expertise in the realm of green hydrogen.
The primary takeaway, echoed by numerous experts, underscores that the hype surrounding hydrogen only becomes meaningful when its role as a catalyst for the revitalization of renewable energy initiatives is accompanied by tangible commercial value.
In numerous regions across Southeast Asia, the availability of national grid power remains limited, with many communities relying on basic living conditions, while others depend on highly polluting diesel generators for energy. Geographical constraints make it impossible to install grid transmission and distribution lines in these areas. How can we overcome this seemingly insurmountable challenge?
Technologists and experts in the renewable energy sector agree that hydrogen fuel cells surpass traditional energy sources due to their key advantages. Emitting only water vapor and heat, hydrogen fuel cells provide a zero-emission energy source with no negative environmental effects, thereby supporting zero-carbon energy strategies. The fuel cells distinguish themselves with their reliability and durability, unlike conventional batteries. They are also versatile and scalable, capable of meeting varying levels of power demand.
Utilizing green hydrogen power through the integration of in situ electrolysis processes and hydrogen fuel cell applications enables independent operation from the grid, providing electricity to rural or off-grid communities. This decentralized approach to power supply offers a sustainable and dependable solution. In alignment with the regional or national power masterplans, a potential solution to rapidly improve living standards and provide electricity to remote areas can be achieved by the implementation of numerous small-scale renewable power generation projects. These projects would independently power villages or communities, establishing off-grid and mini-grid systems that could eventually be interconnected for broader coverage in the future.
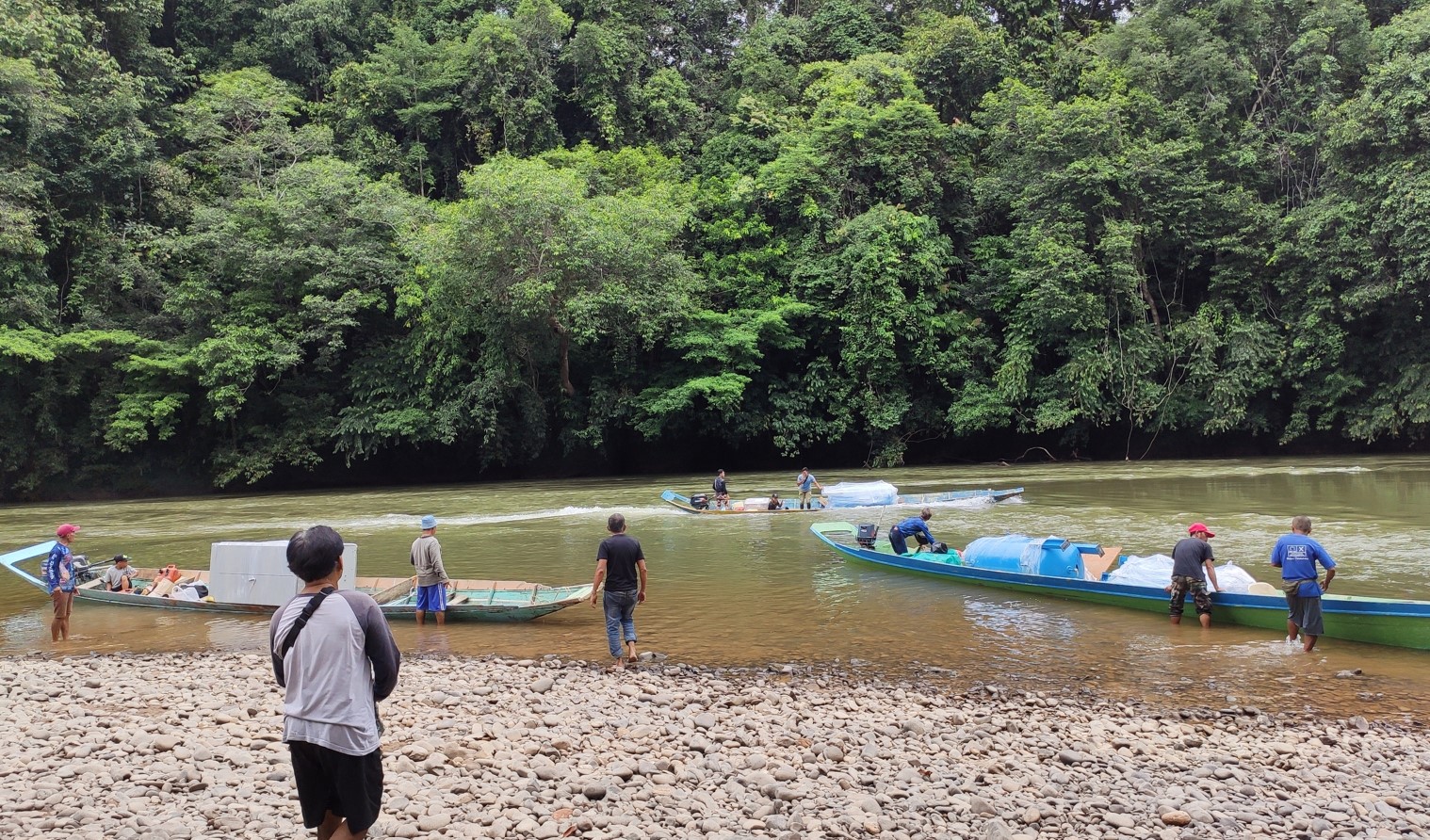


(left) Access to the site location is only possible through the river
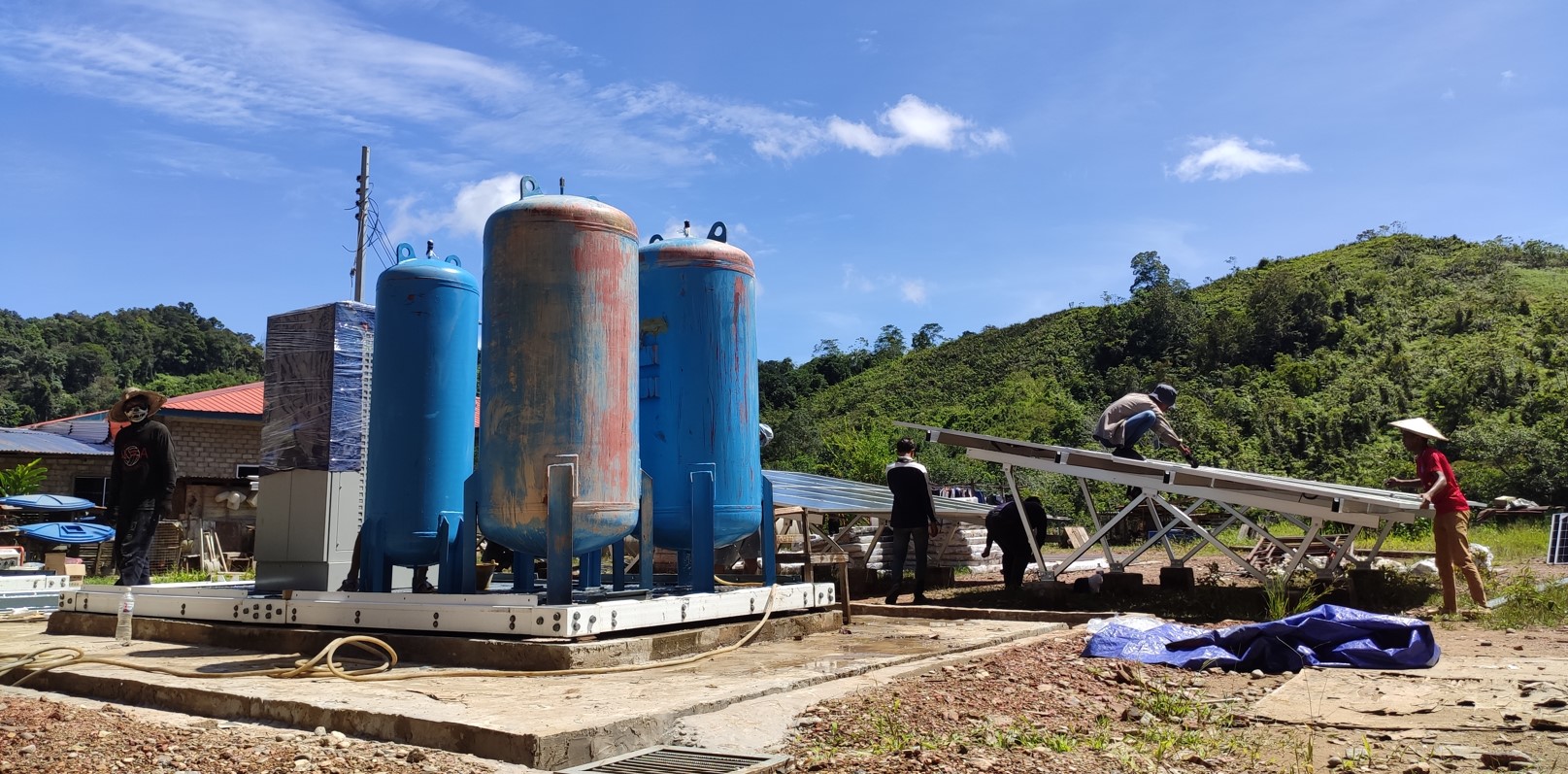
(right)The final hybrid solar hydrogen fuel cell, and their corresponding components are assembled on-site to create a fully functional system
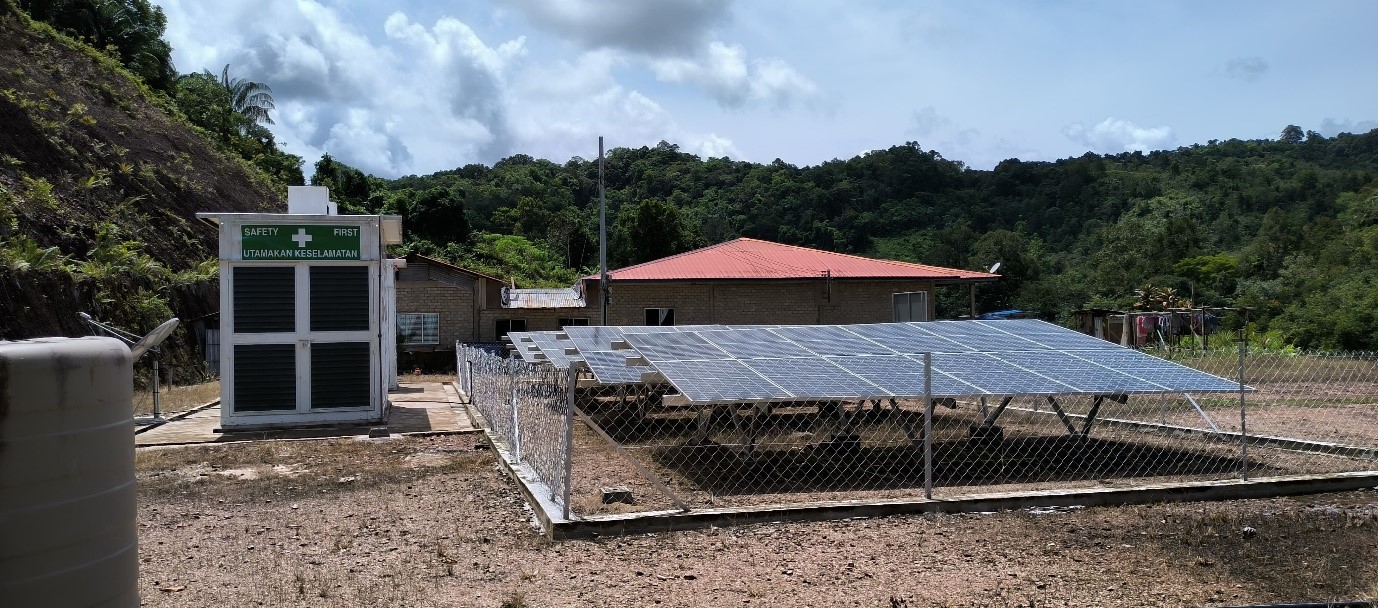
In Malaysia, a hybrid solar and hydrogen fuel cell project was implemented by PESTECH Energy together with a local collaborator, in an off-grid, remote village, achieving operational success by 2023. This is a demonstration of the practicality of an off-grid green hydrogen power concept for rural electrification. With a suitably sized solar system, the site produces green hydrogen, which is then converted into electricity through hydrogen fuel cells to supply power to 20 households. The system utilized Enapter AEM electrolysers and Intelligent Energy fuel cells. The project faced challenges during the transportation and installation of equipment to the site, especially with limited facilities. However, with careful planning, these challenges were successfully overcome.
Diesel generators have been the traditional power source for back-up power when access to the electricity grid has been limited. Intelligent Energy’s IE-POWER fuel cells have provided the project with a zero-emission, diesel replacement and with no reliance on grid connection, they offer a clean, dependable energy source.
The compact and modular POWER unit has been deployed to keep critical applications working in an environment where mains supply is limited.
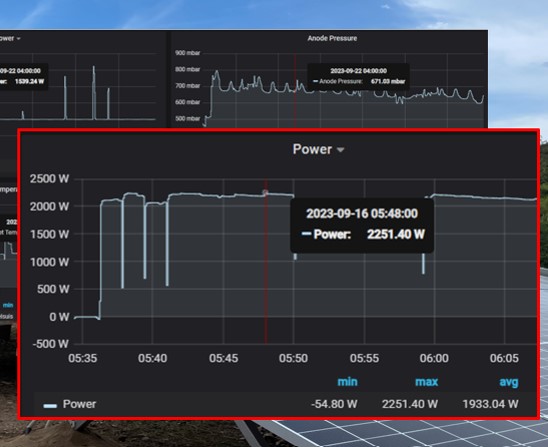
Snap shot of the plant from Enapter Cloud – hydrogen fuel cell output
The success of the project paves a promising route towards realizing a sustainable, efficient, reliable, and clean energy future. Green hydrogen electrification has emerged as a significant contributor to global efforts aimed at reducing carbon footprints and greenhouse gas emissions. Its demonstrated effectiveness in rural electrification and off-grid energy supply is tangible and authentic, rather than merely a facade.
